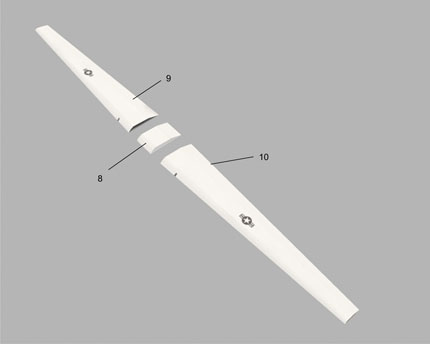
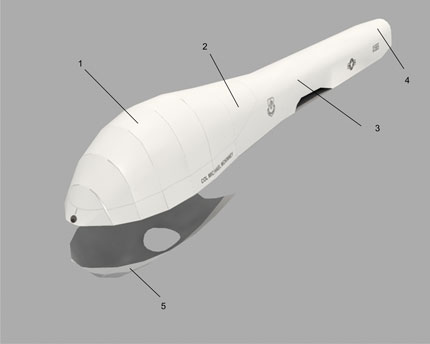
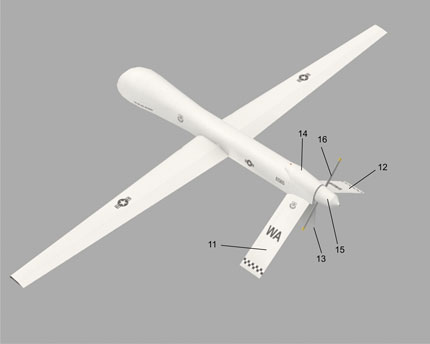
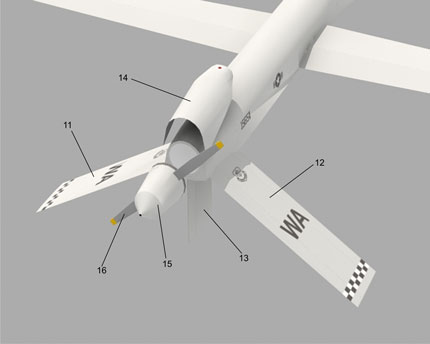
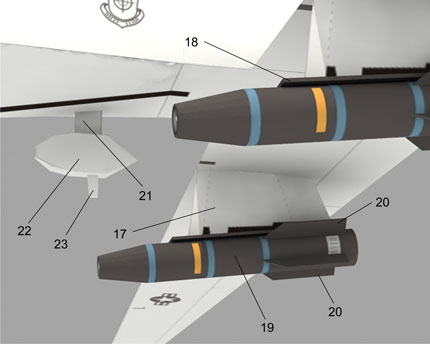
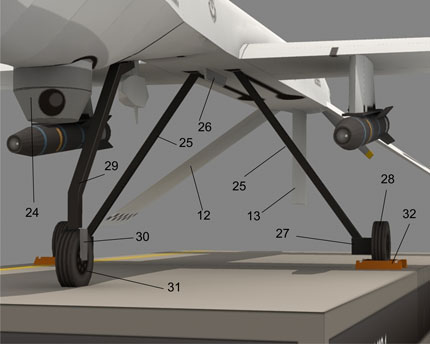
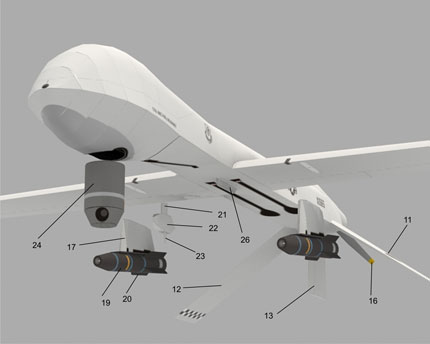
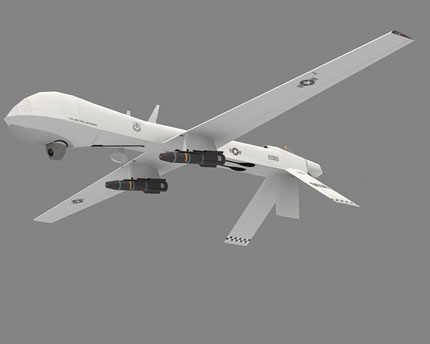
The MQ-1 Predator is an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) which the United States Air Force describes as a MALE (medium-altitude, long-endurance) UAV system. It can serve in a reconnaissance role and fire two AGM-114 Hellfire missiles. The aircraft, in use since 1995, has seen combat over Afghanistan, Pakistan, Bosnia, Serbia, Iraq, and Yemen. It is a remote-controlled aircraft.
The MQ-1 Predator is a system, not just an aircraft. The fully operational system consists of four air vehicles (with sensors), a ground control station (GCS), a Predator primary satellite link communication suite, and 55 people. In the over-all U.S. Air Force integrated UAV system the Predator is considered a "Tier II" vehicle [Wikipedia]
The Predator system was initially designated the RQ-1 Predator. The "R" is the Department of Defense designation for reconnaissance and the "Q" refers to an unmanned aircraft system. The "1" describes it as being the first of a series of aircraft systems built for unmanned reconnaissance. Pre-production systems were designated as RQ-1A, while the RQ-1B (not to be confused with the RQ-1 Predator B, which became the MQ-9 Reaper) denotes the baseline production configuration. It should be emphasized that these are designations of the system as a unit. The actual aircraft themselves were designated RQ-1K for pre-production models, and RQ-1L for production models.In 2005, the Air Force officially changed the designation to MQ-1 (the "M" designates multi-role) to reflect its growing use as an armed aircraft. [Wikipedia]